
Franklin joins the fray Understanding Science
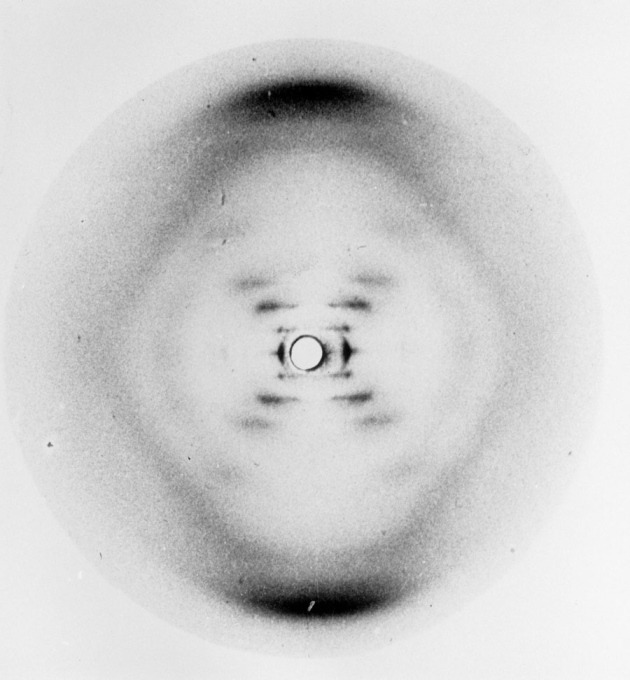
This is the iconic X-ray diffraction photograph of DNA taken by physical chemist Rosalind Elsie Franklin and PhD student Raymond G. Gosling. The genetic material glimpsed in Photo 51 connects all living things and the image thus metaphorically captures human past, present, and future. It also marks an important milestone in science.

Photograph 51 (Xray diffraction image of DNA). Download Scientific
Scientists began collecting X-ray diffraction patterns of DNA in the 1930s before they confirmed that DNA contained genes. William Thomas Astbury, a crystallographer working at the University of Leeds in Leeds, England, gathered the first diffraction patterns of DNA in 1937.
Science Visualized • Rosalind Franklin’s 1952 Xray diffraction image...
(1920-1958) Who Was Rosalind Franklin? Rosalind Franklin earned a Ph.D. in physical chemistry from Cambridge University. She learned crystallography and X-ray diffraction, techniques that she.

XRay diffraction pattern of a DNA oriented fiber under physiological
Photo 51 is an X-ray based fiber diffraction image of a paracrystalline gel composed of DNA fiber [1] taken by Raymond Gosling, [2] [3] a graduate student working under the supervision of Rosalind Franklin in May 1952 at King's College London, while working in Sir John Randall 's group.

Xray diffraction photograph of DNA reproduced in the 40th… Flickr
Introduction In this Post we describe our attempt to replicate the experiment on X-ray diffraction by the DNA molecule. This experimental research, conducted at the time by Rosalind Franklin, allowed us to understand the structure of the DNA molecule.

Photograph 51 (Xray diffraction image of DNA). Download Scientific
Franklin and Gosling's X-ray diffraction image of B DNA, known as Photograph 51.. (X-ray diffraction experiments in the 1930s had inadvertently used a mixture of the A and B forms of DNA.

Astbury’s Xray diffraction photograph of DNA. Reproduced from Astbury
This X-ray diffraction picture of a DNA molecule was Watson's inspiration (the pattern was clearly a helix). Using Franklin's photograph and their own data, Watson and Crick created their famous.

Fossil DNA and XRay diffraction, artwork Stock Image C011/1880
1943: X-ray Diffraction of DNA William Astbury, a British scientist, obtained the first X-ray diffraction pattern of DNA. X-ray diffraction patterns of crystallized molecules can reveal their structures with atomic precision. Astbury obtained X-ray diffraction patterns of uncrystallized DNA.

xrays X ray crystallography, X ray, Dna
Born: July 25, 1920, London, England Died: April 16, 1958, London (aged 37) Subjects Of Study: DNA X-ray diffraction On the Web: University of California - San Diego Supercomputer Center - Rosalind Elsie Franklin (Jan. 05, 2024) See all related content → Top Questions What is Rosalind Franklin best known for?

Discovering the structure of DNA BBC Bitesize
15337. Use of X-ray crstallography to prove that DNA is crystalline, Maurice Wilkins Maurice Wilkins talks about obtaining an X-ray diffraction pattern. ID: 15337 Source: DNAi 16422. Animation 19: The DNA molecule is shaped like a twisted ladder. James Watson and Francis Crick explain how they solved the structure of DNA.

A new look at the BDNA Xray diffraction pattern photo graphed by
A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) or cytosine (C). C and T bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines, while A and G bases, which have two rings, are called purines.

The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale
The pattern of the X-rays bouncing off atoms (a phenomenon called "diffraction") gave information about their location in the molecule. One of the pioneers of this technique, called "X-ray crystallography," was Linus Pauling, who worked at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.

DNA, Xray diffraction Stock Image G110/0636 Science Photo Library
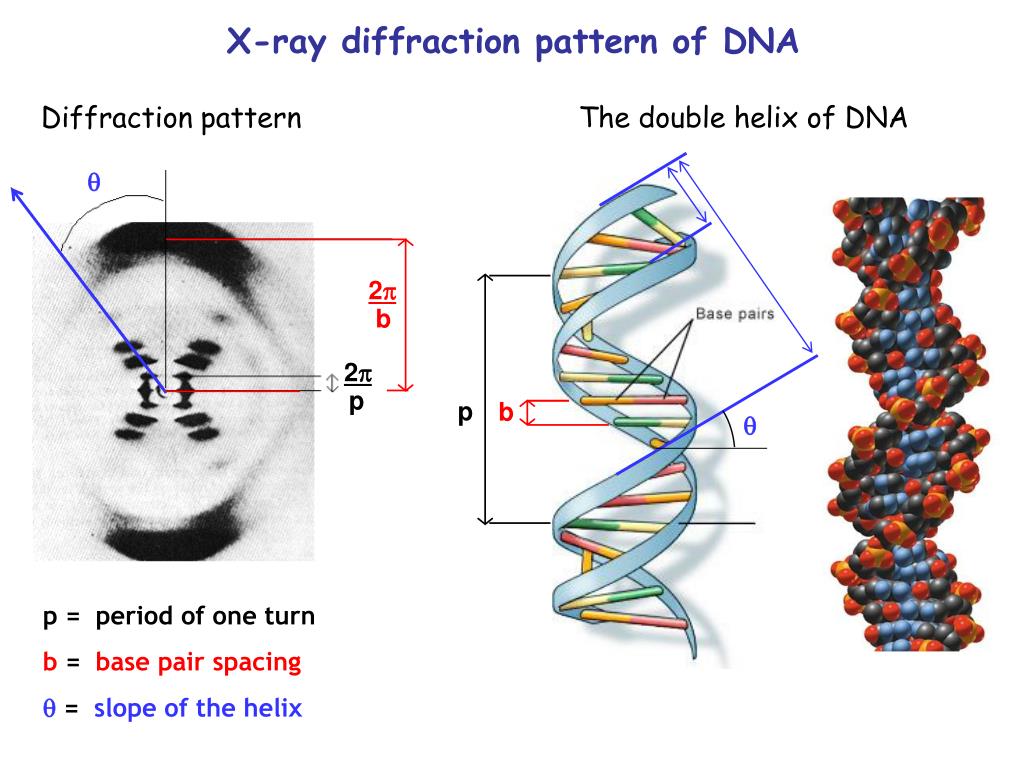
Crick himself had co-authored a paper on the theory of diffraction of X-rays by helices 5. In late 1951, he and Watson combined that theory with what they knew about the chemistry of DNA, and what.

A' form DNA. An example of an Xray diffraction pattern obtained by
Rosalind Franklin Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 1920 - 16 April 1958) [1] was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal, and graphite. [2]
PPT Diffraction Small Features ( ) Reciprocal Space k x = 2 / x
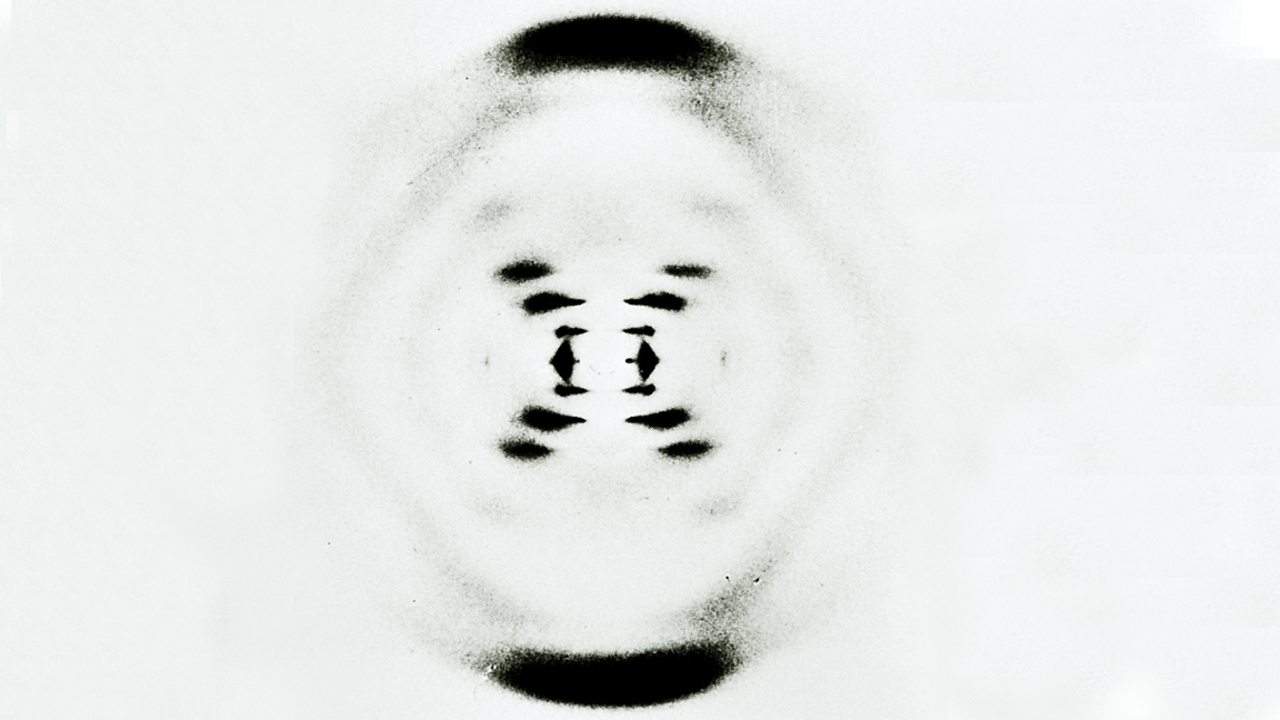
The famous X-ray diffraction pattern obtained by Rosalind Franklin is shown below (2). This X-ray picture stimulated Watson and Crick to propose the now famous double-helix sturcture for DNA. It was surely fortuitous that Crick had recently completed an unrelated study of the diffraction patterns of helical molecules (3).

What is XRay Crystallography? (with pictures)
Rosalind Franklin used X-ray diffraction to determine the structure of DNA molecules. One of her best X-ray pictures is numbered Photo 51 and is shown in Fig. 1 (a). This photo was instrumental to J. D. Watson and F. Crick in deducing the double-helix model of DNA.